Discover Health Chiropractic Webstore
Veg-E Complete Pro™ Vanilla 22oz
Veg-E Complete Pro™ Vanilla 22oz
- A valuable source of several amino acids including the nine essential amino acids
- The blend of organic pea protein, organic pumpkin seed protein, and organic sesame seed protein is a valuable source of several amino acids including the nine essential amino acids
- Supports muscle building and recovery*
- Supports satiety and fullness*
- Supports cellular function and enzyme action*
- Supports energy levels*
- Supports hair, skin, and nails*
- Organic, vegan, gluten-free, non-dairy formula, non-soy formula, non-grain formula
- No genetically engineered ingredients
- No artificial sweeteners or artificial flavors
- Natural flavors made without monosodium glutamate (MSG)
- Excellent source of protein and iron
How does the plant-based protein in this product support health?
Aging adults may benefit from dietary protein intake at 1.0 to 1.5 grams per kilogram per day,1,2,3 which is above the recommended daily allowance (RDA), in order to preserve lean muscle mass and support muscle-building response to exercise.1 The International Society of Sports Nutrition recommends that athletes may benefit from consuming 1.2 to 2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight to support metabolic processes and repair.4 Athletes and those with glucose5 and weight-management6 challenges may benefit from protein supplementation. Protein also plays an important role in cellular function and enzyme action while also supporting hair, skin, and nails.*
Why suggest Veg-E Complete Pro plant-based protein powder for your patients?
The blend of organic pea protein, organic pumpkin seed protein, and organic sesame seed protein is a valuable source of several amino acids including the nine essential amino acids. Veg-E Complete Pro provides 15 grams of vegan protein in a convenient, great-tasting shake.*
Organic Protein Blend
- Organic pea protein concentrate provides a unique vegan source of protein. This protein contains branched amino acids and lysine. Branched-chain amino acids are linked to muscle-building effects in humans.8,9
- Organic pumpkin seed protein contains the sulfur amino acids methionine and cysteine. These are used in the translation process of messenger RNA, which results in building of proteins within the body.10
- Organic sesame seed protein contains the sulfur amino acids methionine and cysteine.*
Suggested Use:
Four heaping tablespoons (scoops) in 8-12 ounces water, one to three servings per day, or as directed. Mix product thoroughly for 10 to 15 seconds. Settling of product after mixing may occur. Store mixed product in refrigerator if not consumed immediately.
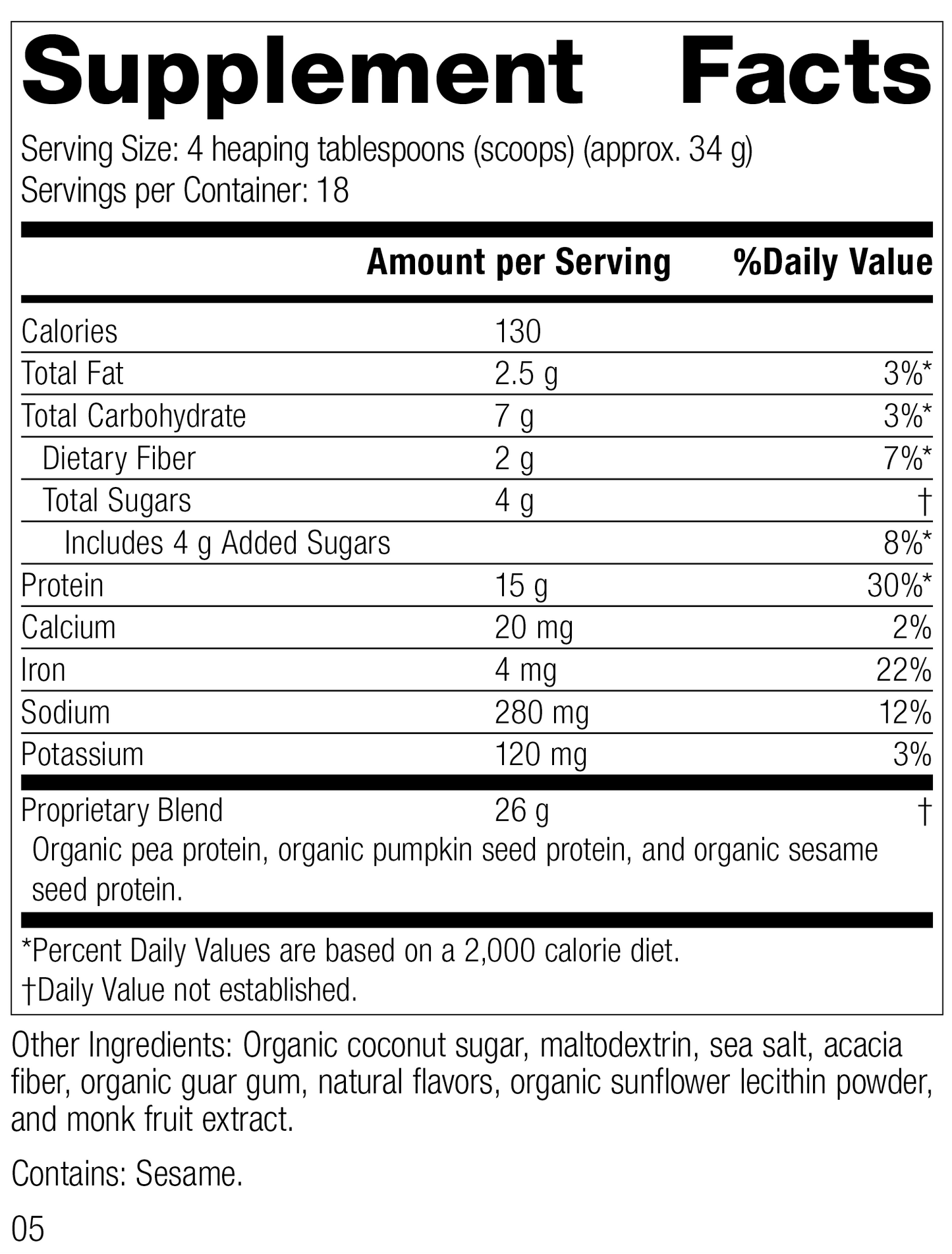
Nutrients & Ingredients
Each Serving Size (4 tablespoons) contains: Calories 130, Total Fat 2.5 g, Total Carbohydrate 7 g, Dietary Fiber 2 g, Total Sugars 4 g, Includes 4 g Added Sugars, Protein 15 g, Calcium 20 mg, Iron 4 mg, Sodium 280 mg, Potassium 120 mg. Proprietary Blend 26 g: Organic pea protein, organic pumpkin seed protein, and organic sesame seed protein. Other Ingredients: Organic coconut sugar, maltodextrin, sea salt, acacia fiber, organic guar gum, natural flavors, organic sunflower lecithin powder, and monk fruit extract. Contains: Sesame.
Please consult the product packaging label for the most accurate product information.
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These Products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Cited References:
- 1. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. 2012. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Food and Nutrition for Older Adults: Promoting Health and Wellness. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2012; 112: 1255-1277.
- 2. Deutz, N, Bauer J, Barazzoni R, et al. Protein Intake and Exercise for Optimal Muscle Function with Aging: Recommendations from the ESPEN Expert Group. Clin Nutr. 2014; 929-36.
- 3. Paddon-Jones D, Rasmussen B. Dietary Protein Recommendations and the Prevention of Sarcopenia. Current Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2009; 12(1): 86-90.
- 4. Campbell B, Kreider R, Ziegenfuss T, et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: Protein and Exercise. J Intl Soc Sports Nutr. 2007; 4:8.
- 5. Gannon, M, Nuttall F, Saeed A, Jordan K, Hoover H. An Increase in Dietary Protein Improves the Blood Glucose Response in Persons with Type 2 Diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003; 78: 734-41.
- 6. Layman D, Boileau R, Erickson D, et al. A Reduced Ratio of Dietary Carbohydrate to Protein Improves Body Composition and Blood Lipid Profiles During Weight Loss in Adult Women. J Nutr. 2003; 133: 411-7.
- 7. Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids. The National Academies Press; 2005.
- 8. Blomstrand E, Eliasson J, Karlsson H, Kohnke R. Branched-Chain Amino Acids Activate Key Enzymes in Protein Synthesis after Physical Exercise. J Nutr. 2006; 136(1): 269S-73S.
- 9. Marangon A, Lacerda V, Corrêa R. Effect of Supplementation of Branched Chain Amino Acids in Muscle Damage Induced by Resistance Training. J Intl Soc Sports Nutr. 2010; 7(Suppl 1): P3.
- 10. Brosnan, J, Brosnan M. The Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids: An Overview. J Nutr. 2006; 136: 1636S-1640S